Building a Clinical Information System (CIS): A Guide for Healthcare Organizations

1 year ago
Have you ever imagined a doctor in an emergency room, trying to make a quick decision but having to sift through piles of paperwork or navigate multiple systems to find a patient’s medical history?
This shouldn’t be the way, right?
With a Clinical Information System (CIS), all that data—past treatments, test results, allergies—is available instantly, in one place.
This kind of system helps doctors, nurses, and healthcare staff focus on what really matters: the patient.
CIS is now a cornerstone of modern healthcare.
It streamlines the way hospitals and clinics operate by organizing vast amounts of patient data.
In fact, over 96% of U.S. hospitals have adopted CIS to keep up with the growing complexity of healthcare.
With data driving more decisions than ever before, CIS helps healthcare providers move beyond guesswork to deliver evidence-based, personalized care.
Simply put, CIS makes healthcare smarter, safer, and faster.
The Problem: Challenges Without a Strong CIS Platform
Without a solid Clinical Information System (CIS), healthcare organizations encounter several issues that impact patient care and efficiency:
1. Data Silos
When departments store patient information separately, it creates data silos.
This fragmentation means clinicians often lack a complete view of patient history, leading to incomplete records and poor communication.
2. Inefficient Workflows
Manual data entry and paper-based processes slow down operations.
Research shows healthcare professionals may spend up to 40% of their time on administrative tasks.
3. Increased Risk of Errors
The absence of a centralized system raises the risk of medical errors.
A study revealed clinical errors in the U.S. cost about $19.5 billion, with over 250,000 deaths attributed to these errors annually, making it the third leading cause of death.
The Solution: How CIS Development Tackles Healthcare Challenges
A CIS acts like a central hub that connects different departments and simplifies processes. Here’s how it helps:
1. Breaking Down Data Silos
A CIS gathers all patient information in one place, creating a complete electronic record. This helps doctors access the information they need to make informed decisions easily.
2. Optimizing Workflows
CIS automates tasks, reducing paperwork and saving time. With features like electronic order entries and scheduling, healthcare staff can focus more on patient care, enhancing productivity and job satisfaction.
3. Enhancing Patient Safety
A CIS boosts patient safety by ensuring data accuracy. It includes checks to prevent errors in medication orders and treatment plans, alerting doctors to potential drug interactions or allergies to avoid mistakes.

Here Are Some Key Components of a CIS Solution that Make It Effective
- Electronic Health Record (EHR): This is where a patient’s complete medical history is stored. It includes everything from medications to test results.
- Computerized Provider Order Entry (CPOE): This lets doctors electronically order tests and medications. It can send alerts to prevent errors.
- Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS): This provides real-time information and recommendations to help doctors make the best decisions at the point of care.
- Results Reporting: This streamlines how lab results and other diagnostics are shared, improving communication between departments.
- Scheduling and Registration: This makes it easier to book appointments and register patients, cutting down wait times.
In critical care areas like the ICU, a CIS can connect with monitors and equipment, giving healthcare teams immediate access to patient information. This real-time data helps improve patient care and team communication.
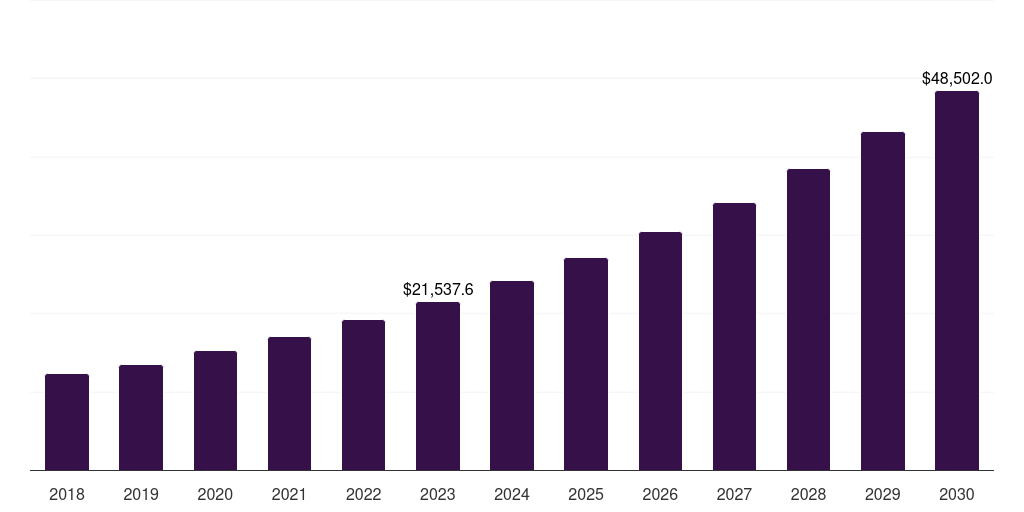
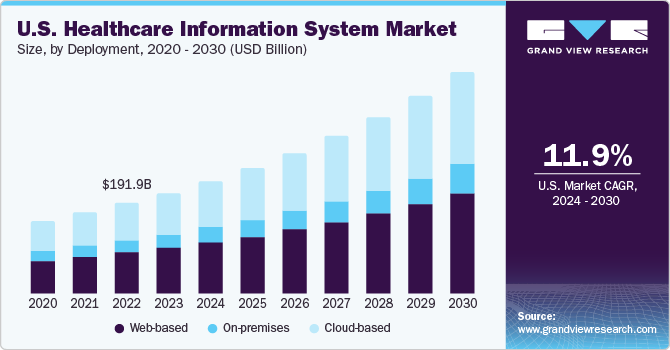
Must-Have Features in an Automated Clinical Information Software
When creating an Automated Clinical Information System (CIS), some features are must-haves for better healthcare delivery. Let’s break them down:
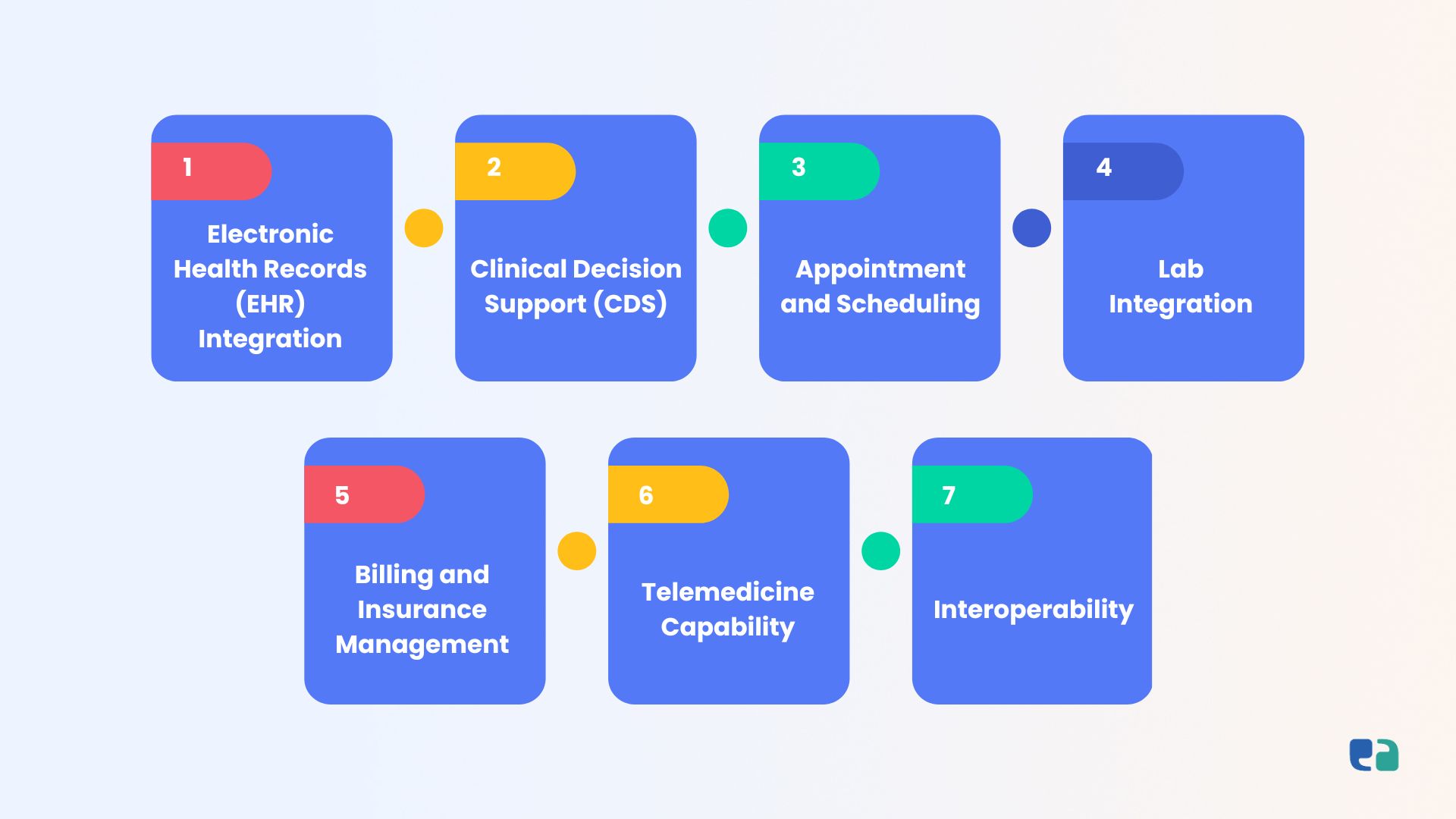
1. Electronic Health Records (EHR) Integration
A good CIS should keep all patient data, histories, and medical records in one place. This makes it easy for doctors to access all the information they need quickly, leading to better care.
2. Clinical Decision Support (CDS)
CDS helps doctors make smarter decisions. It provides alerts and reminders about patient care, reducing errors and supporting evidence-based practices.
3. Appointment and Scheduling
Automating scheduling can lighten the load for staff and doctors. A smart system can reduce no-shows and improve patient flow, making everything run smoother.
4. Lab Integration
Real-time test results are crucial for patient care. A CIS that connects to labs allows healthcare providers to get results quickly, leading to faster diagnoses and treatments.
5. Billing and Insurance Management
Handling claims and billing efficiently is key for any healthcare organization. A good CIS should manage these tasks securely and accurately, minimizing errors.
6. Telemedicine Capability
With telehealth on the rise, having telemedicine features is essential. This allows patients to consult with their doctors remotely, making healthcare more accessible.
7. Interoperability
It’s important for the CIS to connect with other healthcare systems, like pharmacies and labs. This helps share data easily and improves collaboration among providers.
Key Considerations for Successful CIS Development
When developing a Clinical Information System (CIS), several important factors come into play. Let’s break them down:
1. Interoperability and Integration
It’s vital for a CIS to work seamlessly with existing systems in healthcare. Here’s how:
- Legacy Systems: Many organizations have old systems holding valuable patient data. The CIS needs to connect with these to avoid data silos.
- Industry Standards: Using standardized formats and protocols, like HL7, ensures accurate data exchange between systems.
- Data Mapping: Mapping data from different systems into a unified format can be tricky, so careful planning is necessary to avoid inconsistencies.

2. Data Security and Privacy
Protecting patient information is critical. Key steps include:
- Access Control: Only authorized staff should access patient data, using strong methods like multi-factor authentication.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data during transmission and storage keeps it safe from unauthorized access.
- Audit Trails: Keeping detailed logs of data access helps track any suspicious activities.

3. User Interface and Experience
A user-friendly interface is essential for adoption. Here’s what to focus on:
- Intuitive Navigation: Design the system to match clinical workflows, making it easy to navigate.
- Clear Data Display: Present information clearly to help clinicians find what they need quickly.
- Customization: Allow users to personalize their views and set up alerts that suit their workflows.
Make sure it’s mobile-friendly for use on tablets and smartphones in clinical settings.
4. Implementation and Training
A smooth transition to the new CIS requires careful planning:
- Phased Rollout: Introduce the CIS in stages to reduce disruptions and allow for adjustments.
- Comprehensive Training: Provide tailored training for all users to ensure they are comfortable with the system.
- Ongoing Support: Establish a support system to help users and address technical issues as they arise.
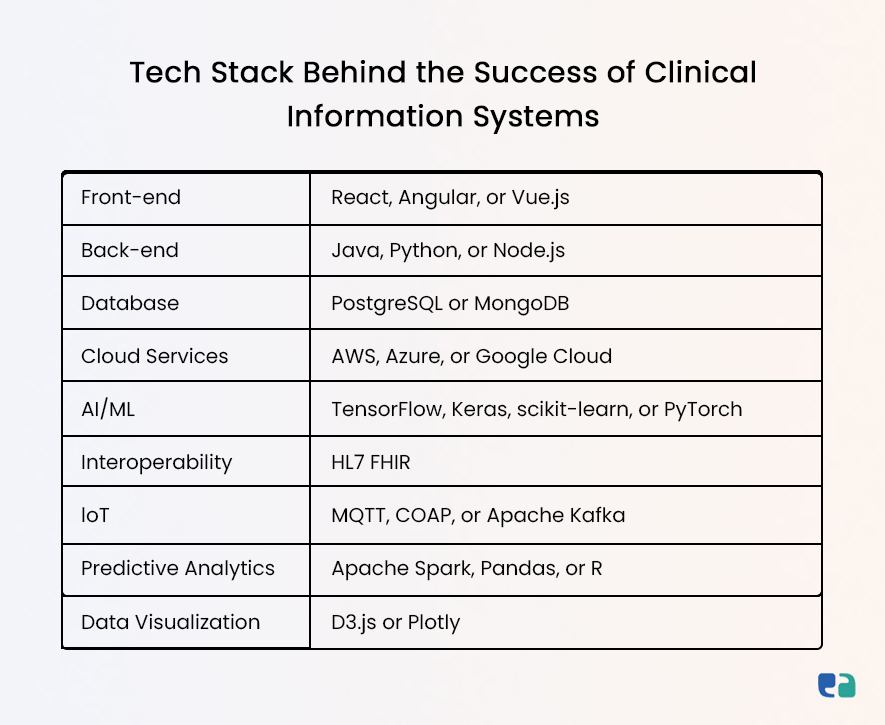
How to Develop a Clinical Information System: 5 Easy Steps
Creating a Clinical Information System (CIS) can feel overwhelming. But it doesn't have to be! Here are five simple steps to guide you through the process:
1. Understand Your Healthcare Needs
Start by diving deep into your specific healthcare environment. Identify the biggest pain points.
Are you struggling with data inefficiencies or documentation issues? What goals do you have for the system? Knowing your end users—like doctors and patients—will help shape the system's design.
2. Choose the Right Type of System
CIS comes in various forms. Decide what you need:
- An Electronic Health Record (EHR) system for patient info?
- A Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS) for making informed decisions?
- A Laboratory Information System (LIS) for lab operations?
Your choice will impact the features and integrations needed.
3. Find a Trusted Development Partner
Partner with a healthcare software development company that knows the ins and outs of clinical systems.
Look for experience with healthcare regulations (like PIPEDA, HIPAA) and a team of experts—developers, UX designers, and more. They should offer end-to-end services, from the first consultation to ongoing support.
4. Define Features and Technology
Now, let's bring your vision to life! Collaborate with your development team to outline essential features. Think about advanced capabilities like AI-driven analytics or integration options.
5. Use Agile Development and MVP Approach
Adopt an agile approach by working in short sprints. This allows for quick development and constant feedback from healthcare stakeholders.
Start with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to test your ideas and gather user feedback. Prioritize testing for functionality, security, and compliance before deployment.
Real-World CIS Implementation Examples
Let's look at some real-world examples of Clinical Information Systems (CIS) in action. These cases show how CIS can make healthcare better.
1. Critical Care CIS Initiative in Ireland
In Ireland, there's a big push to implement a CIS for critical care beds that currently don’t have one. The goal is to standardize how critical care data is collected and managed across the country.
Features: This initiative will likely use a standard CIS that connects to existing hospital systems. It will include electronic health records, computerized order entry, clinical decision support, and results reporting designed for critical care.
Benefits: The aim is to improve patient care and safety by making data more available and accessible. This helps doctors make better decisions and improves workflows.
2. Other Notable Examples
Many other CIS systems are popping up across Ireland’s healthcare. Here are a few:
- National Integrated Medical Imaging System (NIMIS): This system helps manage and share medical images digitally, speeding up diagnoses and improving collaboration among radiologists.
- Kidney Disease Clinical Patient Management System (KDCPMS): Designed for kidney patients, this system tracks disease progression, manages treatment plans, and coordinates care among providers.
- Maternal & Newborn Clinical Management System (MN-CMS): This system focuses on mothers and newborns. It offers tools for managing electronic health records, prenatal monitoring, and postnatal care.
Looking Ahead: Emerging Trends in CIS Development
The future of Clinical Information Systems (CIS) is filled with exciting possibilities that can transform healthcare. Here are some key trends to watch:
1. AI and Machine Learning
AI and ML are making systems smarter. They can help doctors diagnose faster, predict health risks, and even answer patients' basic health questions through chatbots. These tools lighten the load on healthcare professionals and improve patient care.
2. Internet of Medical Things (IoT)
IoT connects medical devices and wearables to the CIS, creating a more connected system. Sensors track patient vitals in real time, while smart devices can manage medications and reduce errors.
3. Virtual Wards and Chatbots
Virtual wards allow patients to be monitored from home, cutting down on hospital visits. Meanwhile, chatbots in CIS handle routine tasks and offer patient support, improving efficiency.
These trends show how CIS is evolving to provide smarter, more patient-focused care.

