Implementing Cloud Computing in Healthcare Enterprise Systems: From Strategy to Execution

2 months ago
In Canada, healthcare organizations are feeling the pressure to improve patient care while keeping costs down.
But outdated IT systems often get in the way, making it hard to grow and adapt.
On top of that, there’s a need for better data security, smooth system connections, and access to new technologies like AI and IoMT.
Well, cloud computing can help with all of this.
It allows healthcare organizations to scale up, improve patient care, and keep data secure.
But you know, moving to the cloud isn’t always easy.
In this blog, we’ll show you a simple, step-by-step guide to help you move from planning to successful execution, so your healthcare organization can make the most of cloud computing.
What is Cloud Computing in Healthcare?
Cloud computing in healthcare means using remote servers on the internet to store, manage, and process healthcare data.
This allows healthcare organizations to access resources like storage, processing power, and applications whenever needed, without relying on local servers or physical infrastructure.
With cloud computing, healthcare providers can manage patient records, collaborate easily, and deploy applications, all while ensuring flexibility, scalability, and security.
Market Overview
The global healthcare cloud computing market is currently worth $58.93 billion and is expected to grow significantly. By 2030, it could reach $170.82 billion. This growth is fueled by the cloud’s ability to:
- Manage patient records at scale
- Support telemedicine
- Enhance data security
In 2023, 70% of healthcare organizations adopted cloud computing. This shift is driven by factors like:
- More investment in SaaS software
- Real-time big data analytics
- Growth in remote patient monitoring
- Use of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- Integration of AI and machine learning
Technological Foundations for Cloud-Powered Healthcare
Cloud computing in healthcare relies on different models to help organizations choose the right infrastructure and services. Let’s break it down.
Core Cloud Computing Models
There are two main categories of cloud computing models: deployment types and service models.
1. Deployment Types:
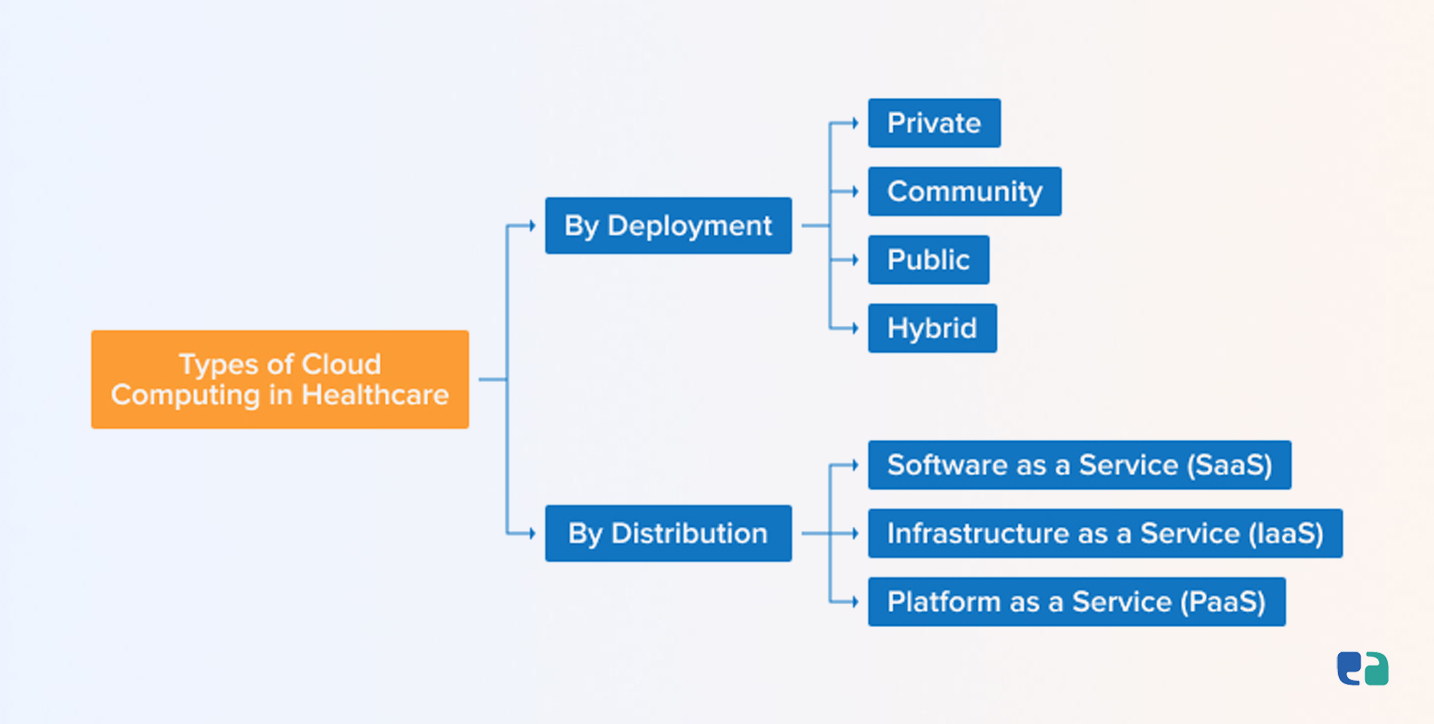
- Public Cloud: Managed by third parties and available to everyone. It’s cost-effective, but security and compliance can be a concern for some healthcare organizations.
- Private Cloud: Exclusively for one organization, providing greater control over security but at a higher cost.
- Community Cloud: Shared by organizations with similar needs, offering a balance of public and private cloud benefits.
- Hybrid Cloud: Combines different cloud types for flexibility. It’s popular with healthcare providers because it optimizes cost, security, and performance.

2. Service Models:
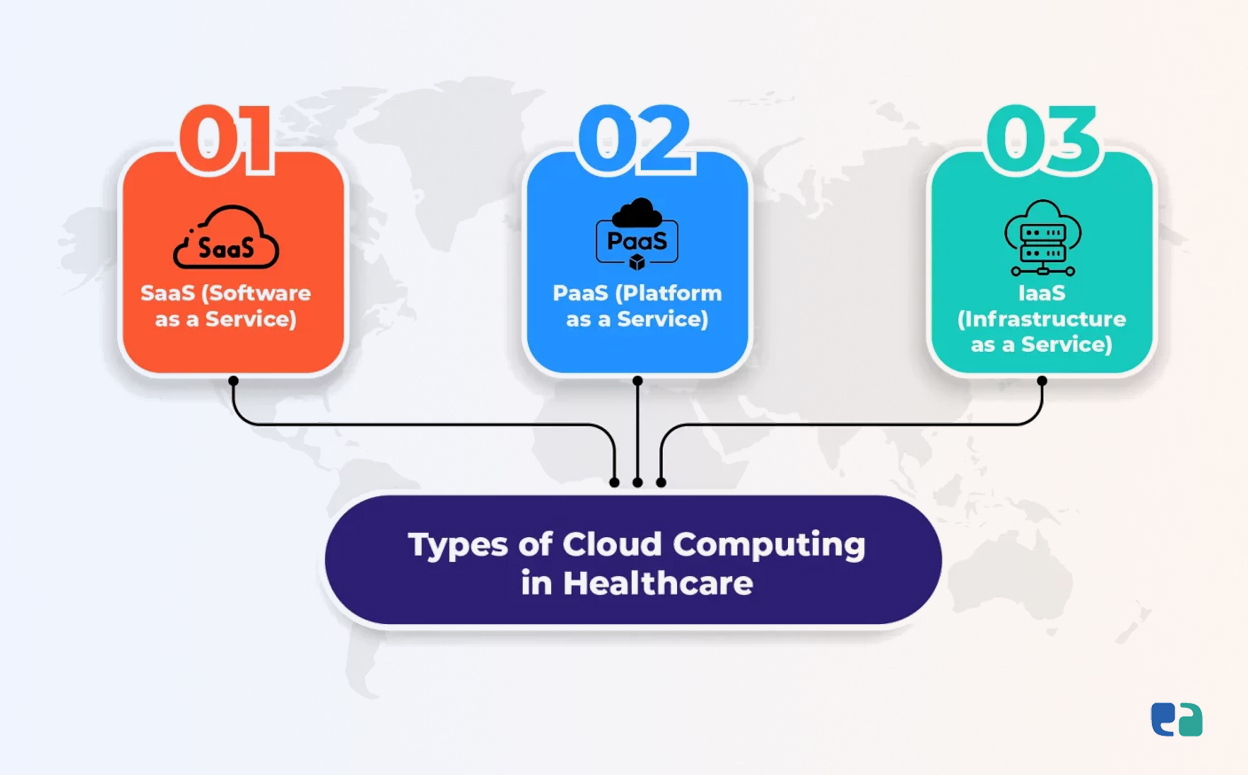
- SaaS (Software as a Service): Cloud-based software applications. Providers manage everything, making it easy and affordable for healthcare organizations.
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): Provides access to computing resources like storage and servers. It offers more flexibility and control.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): A platform for developing and deploying applications. It allows healthcare organizations to focus on building apps without worrying about underlying infrastructure.
Enabling Technologies
1. IoMT (Internet of Medical Things):
IoMT connects medical devices to the internet, enabling real-time data collection and remote monitoring. Cloud computing helps manage and analyze the large amounts of data generated by these devices, improving healthcare delivery.
2. AI and ML (Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning):
AI and ML are transforming healthcare with better decision-making and automation. Cloud platforms provide the computing power needed to run AI/ML models that:
- Improve Diagnostics by analyzing large datasets.
- Predict Health Risks and Outbreaks.
- Personalize Treatments based on patient data.
3. Edge Computing:
Edge computing processes data closer to its source, reducing delays. This is especially useful for real-time applications like remote surgery and intensive care monitoring, enabling faster responses in critical situations.
These technologies help healthcare organizations boost efficiency, improve patient care, and make better decisions.

Use Cases and Applications of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cloud computing is making a big impact in healthcare, offering both traditional and advanced solutions that improve care.
Traditional Areas
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): Cloud-based EHR systems, like eKlinik, securely store and share patient data. They help hospitals globally access patient records, reduce paper records, and comply with regulations like HIPAA.
- Telemedicine: Cloud platforms enable remote consultations and monitoring. They allow patients in remote areas or with limited mobility to receive care, cutting down on in-person visits and reducing costs.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: IoMT devices and cloud solutions track patient data remotely. This helps healthcare providers manage chronic conditions like diabetes and heart disease, while also reducing hospital readmissions.
Advanced Applications
- Genomic Research: Cloud computing supports large-scale genomic analysis, helping researchers develop personalized medicine and accelerating breakthroughs.
- Predictive Analytics: AI-powered predictive tools analyze patient data to forecast health events, allowing early intervention and better resource allocation.
- AI Diagnostics: Cloud-based AI tools enhance diagnostic accuracy by analyzing medical images and patient data, leading to quicker, more accurate diagnoses and better outcomes.
Strategic Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
- Cloud computing helps healthcare organizations reduce IT costs by eliminating the need for expensive hardware, with some providers saving up to 40%. KPJ Healthcare Berhad in Malaysia expects long-term savings of 30-40% through cloud adoption.
- Cloud services allow healthcare organizations to scale resources quickly, especially during high-demand times like flu season or pandemics.
- Real-time data analysis through cloud platforms helps predict health issues and optimize resource allocation. For example, Canada’s diagnostic imaging repositories enable secure, up-to-date data sharing for better patient care.
- Cloud computing improves patient access and engagement by supporting telemedicine, remote monitoring, and personalized care, with 81% of patients expecting a patient-centric approach.
- It accelerates research by providing scalable resources for data analysis and collaboration, fostering innovation in areas like drug discovery and AI-powered diagnostics.
- Cloud platforms support emerging technologies such as AI, machine learning, and IoMT, improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment quality.
Case Studies: Cloud Computing in Healthcare
1. Brant System

Brant Community Healthcare System in Ontario became the first Canadian organization to adopt a fully managed, cloud-based EHR, MEDITECH as a Service (MaaS), hosted on Google Cloud.
The decision, driven by a small IT team and the need for enhanced security, eliminates the need for costly hardware and redundant data centers.
This cloud solution provides continuous monitoring, backups, and remote access to patient records, improving efficiency and patient care.
With features like physician order entry and electronic medication reconciliation, the system streamlines workflows and enhances safety, marking a significant step toward digital transformation in healthcare.
This Malaysian healthcare provider uses cloud computing to reduce IT costs and improve collaboration across hospitals.
Their cloud system enhances security, speeds up services, and improves operational efficiency.
This Malaysian company offers eKlinik, a cloud-based healthcare system that provides real-time information to patients, doctors, and hospitals.
Their cloud-based EMR system makes medical data accessible and sharable across hospitals, improving emergency care.
Key Challenges and Lessons Learned in Cloud Adoption for Healthcare
While cloud adoption brings many benefits, there are challenges along the way. Here’s what organizations learned:
1. Security Concerns: Cloud migration raises concerns about securing sensitive patient data. Healthcare organizations can address these by:
- Choosing reputable vendors with strong security measures.
- Using network segmentation to enhance security.
- Training staff on security protocols and responsible data handling.
2. Cloud Management: Managing cloud environments can be tough due to a lack of expertise. To solve this:
- Invest in skilled cloud professionals or collaborate with experienced partners.
- Embrace automation and Infrastructure as Code to simplify management.
3. Cloud Availability: Cloud downtimes, though rare, can happen. Mitigate this risk by:
- Implementing multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategies for backup and redundancy.
4. Unrealized Cloud Potential: Some healthcare organizations view cloud computing only as a cost-saving tool. To fully harness its power, organizations should integrate the cloud with emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and automation for a comprehensive digital transformation.

Ensuring Security and Compliance in Healthcare Cloud Computing
Security and compliance are vital for healthcare cloud computing, especially under regulations like HIPAA (US), GDPR (EU), and PIPEDA (Canada).
These laws ensure patient data remains protected and private. However, the sector faces growing threats, with 725 cyberattacks reported globally in 2023.
Common risks include malware, phishing, and denial-of-service attacks, which can lead to breaches, financial losses, and reputational harm.
To address this, healthcare organizations encrypt data, implement multi-factor authentication, and conduct regular security audits.
In Canada, compliance with PIPEDA is critical for protecting personal health data.
Selecting trusted cloud providers with strong security certifications and compliance measures further ensures sensitive information is safe.
These steps help healthcare organizations balance innovation with robust data protection.

How Cloud Computing is Shaping the Future of Healthcare: Trending Technologies
Cloud computing is driving the integration of advanced technologies in healthcare.
- Blockchain ensures secure and tamper-proof medical records. It also helps track medication supply chains, improving transparency and reliability in patient care.
- AI Diagnostics are advancing quickly. For instance, predictive analytics using AI has detected heart risks by analyzing ECG results. AI-driven tools also make diagnosis faster and more accurate by analyzing medical data.
- Augmented Reality (AR) supports surgeries by offering detailed 3D visualizations. It also enhances patient education through interactive tools.
- Decentralized Care is expanding with cloud-enabled telemedicine and remote patient monitoring. This makes healthcare accessible to rural areas, reducing hospital visits and empowering patients.
- Personalized Medicine uses big data and AI to tailor treatments. Genomic and lifestyle data are analyzed on cloud platforms to create precise care plans.
Cloud computing is the backbone of this technological transformation, ensuring healthcare is smarter, safer, and more patient-focused.
Implementation Strategies for Cloud Computing in Healthcare: 5 Step Process
Adopting cloud computing in healthcare requires careful planning and execution. Here’s how to make the transition smooth:
1. Clear Migration Plan
Define your goals, like cutting costs or enhancing security.
Assess your current IT setup to see what needs migration.
Break the process into steps, starting with the most critical systems. For example, prioritize migrating patient management systems before less-used applications.
2. Pick the Right Cloud Vendor
Choose a provider experienced in healthcare.
Look for certifications like HIPAA compliance.
Ensure their services can scale as your needs grow. Check if their pricing aligns with your budget. Reliable support services, including troubleshooting, are a must.
Choosing the right cloud vendor can be challenging. Talk to our tech experts for a free consultation and find the perfect fit for your needs.
3. Manage Change Effectively
Communicate the benefits of cloud migration with your team.
Offer training on how to use new tools and workflows. Provide ongoing support to address concerns.
4. Train Your Team
Focus on security practices, like using strong passwords.
Teach staff to manage data safely within the cloud. Help them adapt to new workflows, ensuring seamless operations.
By following these steps, healthcare organizations can embrace cloud computing with confidence, boosting efficiency and staying innovative.
Ready to Harness the Power of Cloud Computing in Healthcare?
Cloud computing has huge potential to transform healthcare. It can improve patient care, boost efficiency, reduce costs, and spark innovation.
But adopting the cloud isn't always straightforward.
It requires careful planning and expert support. Here's how we can help you navigate the process:
- Create a Cloud Strategy: We’ll help you build a strategy that fits your needs, goals, and challenges, ensuring a smooth transition.
- Choose the Right Vendor: With our expertise, we’ll guide you in selecting the best cloud provider for your security, scalability, and compliance needs.
- Seamless Migration: We’ll manage the technical side of things, making your move to the cloud smooth and secure.
- Ensure Security & Compliance: We’ll set up strong security measures to protect patient data and meet all regulations.
- Staff Training: We’ll train your team so they can confidently use the new cloud system.
- Innovate with New Tech: Cloud computing allows you to integrate AI, IoT, and automation to enhance care and efficiency.
Don't let the complexities of cloud adoption hold you back.
Contact us today and talk with our cloud computing experts for your healthcare needs
